With the continuing surge of drug abuse, overdose, and addiction happening today, companies and even federal agencies are cracking down on addictive substances like never before.
“Relapse is part of Addiction Recovery – Our Drug Rehab Program helps you create a relapse prevention plan”
Changes like mandatory hair drug testing for safety-sensitive transportation employees, institutionalized crackdowns on college drug sharing, and even government subsidies to cover the costs of overdose-reversing medications for schools and businesses are becoming the norm. And since drug use has become so rampant today, more people than ever are wondering about how long these dangerous substances stay in the body – whether they’re preparing for an interview or are trying to figure out withdrawal timelines so they know what to expect during detoxification. No matter why you’re looking for info on how long these drugs stay in your system, this complete guide will help.
Not Everyone’s the Same
Just like with addiction in general, not everyone’s body will process addictive substances the same. Body weight, genetics, individual health, and so many other factors all come into play in how long these drugs stay in your system. And on top of that, the body metabolizes different drugs and alcohol in different ways too. As a result, each drug will stay a different length of time in your body. The drugs are detectable in your urine, blood, oral fluids and hair. The drug detection test for each drug will vary as well. Here are the top 10 illicit drugs used by addicts, and the amount of time that they stay in your system.
Meth: A Long-Lasting & Terrifying Stimulant
Also known as meth or crystal meth, methamphetamine is deadly, highly addictive, and incredibly dangerous both for users and those around them. It’s usually smoked or injected, but some people also get high on the drug by swallowing it as a pill or snorting it. Meth abusers often go on days-long binges on the drug called “runs.” These runs can lead to serious health problems like dehydration and malnutrition – not to mention the infamous “meth mouth” that can often develop after chronic use.
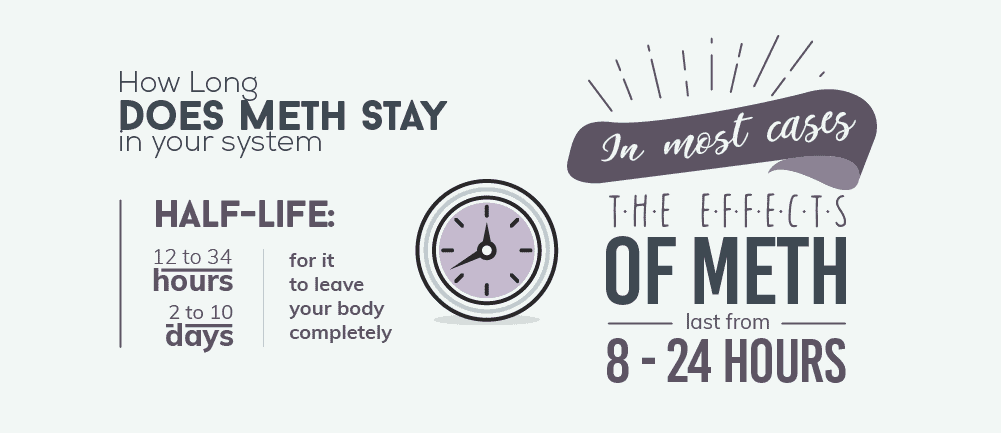
How Long Does Meth Stay in Your System
Methamphetamine enters and exits the body quite slowly. Meth has a plasma half-life of anywhere from 12 to 34 hours. This means that the concentration of the drug in your blood will be halved after 12 to 34 hours. It takes anywhere from 2 to 10 days for it to leave your body completely. The length of time that it takes will be dependent on:
- The concentration of the dose taken
- The purity of the dose taken
- The amount of meth ingested
- The ingestion method
- The way that the body metabolizes the drug
In most cases, the effects of meth will last anywhere from 8 to 24 hours. Meth can be detected in urine tests for up to 5 days after last use.
Side Effects of Using Meth
Some of the short and long-term side effects of meth abuse according to NIDA include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Increased wakefulness and physical activity
- Decreased appetite
- Faster breathing
- Rapid and/or irregular heartbeat
- Increased blood pressure and body temperature
Long-Term Side Effects
- An increased risk of bloodborne pathogens like HIV or Hepatitis
- Extreme weight loss
- Severe dental problems (“meth mouth”)
- Intense itching, leading to skin sores from scratching
- Anxiety
- Confusion
- Sleeping problems
- Violent behavior
- Paranoia—extreme and unreasonable distrust of others
- Hallucinations—sensations and images that seem real though they aren’t
Cocaine: A Party Drug with Deadly Side Effects
Cocaine has long been one of the most popular party drugs in the country, leading it to disproportionately affect the younger population more than middle-aged adults. It’s also been shown to have a clear connection with alcohol abuse as well. Cocaine comes in both a powdered form (which abusers will typically snort or inject) and a solid rock form that’s typically smoked known as “crack.”
How Long Does Cocaine Stay in Your System
Cocaine has one of the shortest half-lives out of all the drugs out there. Its half-life is only about an hour to an hour and a half. This stimulant is two times more likely to be abused by men than women. Although it has a relatively short half-life, the drug does take quite some time to metabolize. The drug is easily detectable via a urinalysis, a blood and saliva drug test, and a hair drug test. It can usually be detected via a urinalysis 2 to 4 days after last use. For chronic users, urine drug tests can still be positive up to 12 days later. Chronic users who took high doses may even have positive urine tests for up to 3 weeks. It’s possible to detect cocaine in a user’s blood and saliva anywhere from 12 to 48 hours after its last use. It remains in the hair for years, and traces of cocaine linger in a person’s sweat for several weeks as well.
When Do Levels of Cocaine Peak in Blood Plasma
The strength of the high obtained from cocaine will depend on the dosage taken and the purity of the drugs. The average purity of street cocaine is about 65.1%. However, it’s not unusual for addicts to come across some extremely pure samples. In most cases, the effects of cocaine will last about 20 to 30 minutes. The moment when the concentration in blood plasma reaches peak levels will vary depending on the mode of administration. Users can expect levels to peak:
- About 30 minutes after snorting the cocaine
- Around an hour after orally taking the narcotic
- Approximately 5 minutes after injecting it
- About 45 minutes after smoking the drug
It’s important to note that cocaine can accumulate within the body of chronic users. In these cases, it may take only a short while for the drug levels to peak and longer for it to be fully metabolized.
Side Effects of Abusing Cocaine
Both crack and cocaine have a variety of short-term and long-term side effects. According to NIDA, these side effects include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Extreme happiness and energy
- Mental alertness
- Hypersensitivity to sight, sound, and touch
- Irritability
- Paranoia—extreme and unreasonable distrust of others
- Nausea
- Raised blood pressure and temperature
- Irregular heartbeat
- Tremors and muscle twitches
- Restlessness
Long-Term Side Effects (based on the method of administration)
- Snorting: loss of smell, nosebleeds, frequent runny nose, and problems with swallowing
- Smoking: cough, asthma, respiratory distress, and a higher risk of infections like pneumonia
- Consuming by mouth: severe bowel decay from reduced blood flow
- Needle injection: higher risk for contracting HIV, hepatitis C, and other bloodborne diseases, skin or soft tissue infections, as well as scarring or collapsed veins
“We accept many health insurance plans. You can get your life back in order with our outpatient program today!”
Hydrocodone: A Powerful Prescription Pain-Reliever
Sold under the brand names Hysingla ER, Zohydro ER and Vicodin, hydrocodone is a popular prescription painkiller used in treating moderate to severe pain that isn’t responding to other medications. 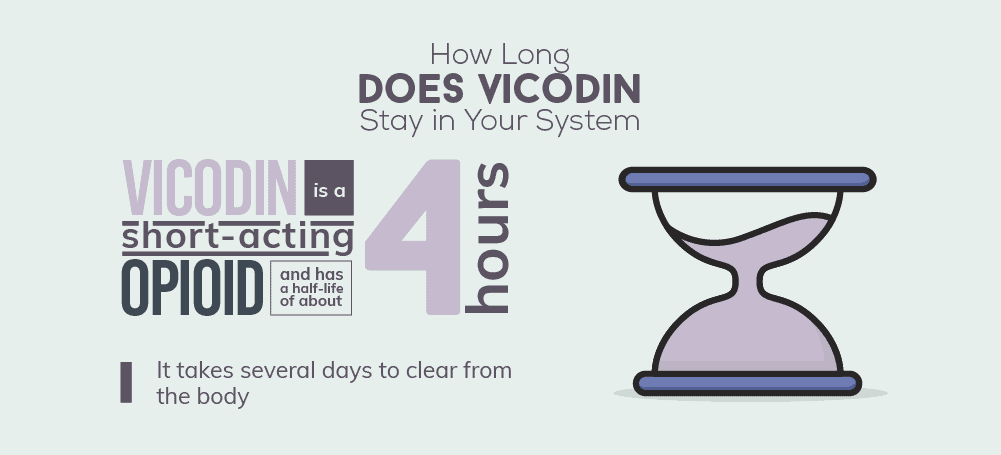 And while it typically only comes from a doctor, hydrocodone is also often sold on the streets just like so many other kinds of opioid pain relievers. Legal prescription drugs like hydrocodone are actually some of the major driving forces behind the ever-raging opioid epidemic – a health crisis that kills more than 115 Americans every single day.
And while it typically only comes from a doctor, hydrocodone is also often sold on the streets just like so many other kinds of opioid pain relievers. Legal prescription drugs like hydrocodone are actually some of the major driving forces behind the ever-raging opioid epidemic – a health crisis that kills more than 115 Americans every single day.
How Long Does Hydrocodone Stay in Your System
Opiates like hydrocodone are also one of the most frequently abused drugs used by addicts. In comparison to other opiates, hydrocodone leaves the body quite quickly. It has a half-life of about 3.8 hours and will be completely excreted from the body after 20.9 hours. Hydrocodone metabolizes into many metabolites. In particular, it metabolizes into a substance known as norhydrocodone. It takes quite a bit longer for the body to metabolize this substance. In fact, the body may not clear the substance for up to 2 days. Hydrocodone remains in the saliva for 12 to 36 hours after the last capsule is taken. It remains in the urine for 2 to 4 days and lingers in the hair for up to 90 days.
Interactions with Other Drugs
It can take even longer for the body to clear Vicodin if other drugs are being used. Vicodin may interact with other drugs like:
- Alcohol
- Antihistamines, like cetirizine
- Cough relievers like codeine
- Drugs that induce sleep like lorazepam
- Marijuana
- Mixed opioid agonists and antagonists, like butorphanol
- Muscle relaxants, like cyclobenzaprine
- Naltrexone
Mixing Vicodin with other drugs can even become deadly.
Side Effects of Hydrocodone Abuse
According to Everyday Health (short-term) and the Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders (long-term), some of the most prevalent side effects of hydrocodone abuse include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Weak or shallow breathing
- Pain or burning when you urinate
- Confusion, tremors, severe drowsiness
- A light-headed feeling, like you might pass out
- Infertility, missed menstrual periods
- Impotence, sexual problems, loss of interest in sex
- Low cortisol levels–nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, dizziness, worsening tiredness or weakness
Long-term Side Effects
- Chronic and serious constipation
- Frequent nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal cramping
- Bloating
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Sleep apnea
- Respiratory depression
- Low blood pressure
- Abnormally slow heartbeat
- Increased pain sensitivity
- Depression and other mental illnesses
Xanax: An Antidepressant That’s Highly Addictive
This is one of the most widely prescribed drugs for mood disorders in the country. It’s typically used to help treat depression and anxiety. And when used properly, it can be incredibly helpful. However, Xanax and other benzodiazepines are increasingly becoming a dangerous substance of abuse. And overdose rates involving these drugs has soared in recent years – they’re now involved in around 30% of all overdoses across the country. And when you combine that with one of the most uncomfortable withdrawal syndromes out of any drug being used today (even worse than heroin according to some), this is one highly dangerous and highly addictive drug that most people aren’t scared enough of.
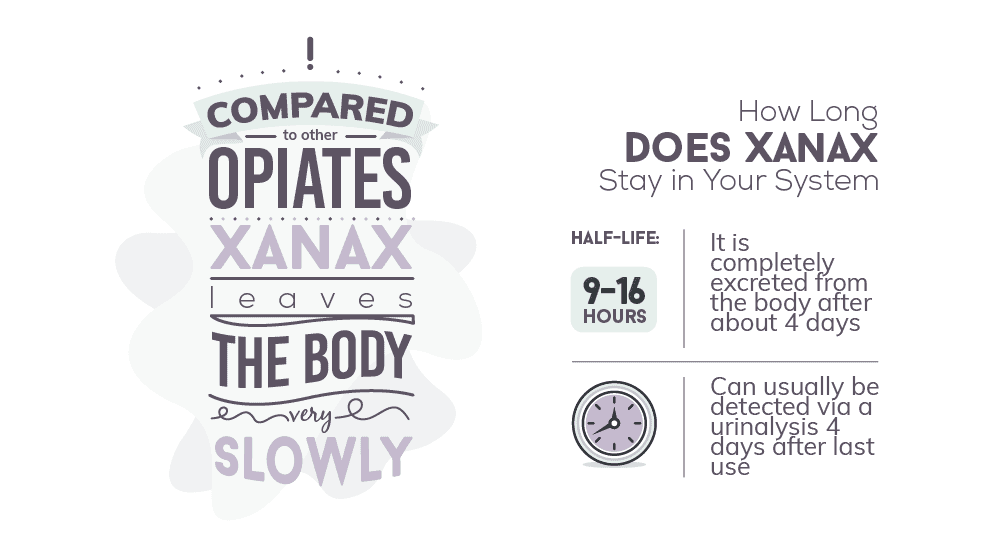
How Long Does Xanax Stay in Your System
When compared to other illicit drugs, the body takes a much longer time to get rid of Xanax. Xanax is one of the most popular drugs in the benzodiazepine class. Similar to other benzos like Klonopin, it has a calming and relaxing effect on the body. With that said, Xanax has an approximate half-life of around 9 to 16 hours. This means that it will stay in one’s system for about 4 days. Even in small doses, this narcotic can be detected in one’s blood, saliva or hair for up to a week. Users can still test positive with a urinalysis 4 days after their last use and 2.5 days with a saliva test. Xanax use can be detected in the blood for up to 1 day after its last use as well.
Factors that Affect How Long Xanax Stays in the Body
There are many factors that determine the rate at which a body metabolizes Xanax. Some of these factors include the person’s:
- Age
- Body fat content
- Height and weight
- Kidney condition
- Liver condition
- Metabolic speed
It can also be dependent on factors like the amount of Xanax taken, and the length of the drug use.
Side Effects of Xanax Abuse
According to NIDA (short-term effects) and the Journal of Behavioural Neurology (long-term), some side effects of abusing Xanax include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Slurred speech
- Poor concentration
- Confusion
- Headache
- Light-headedness
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Problems with movement and memory
- Lowered blood pressure
- Slowed breathing
Long-Term Side Effects
- Aggressive behavior
- Impaired psychomotor performance
- Altered cognition
- Poor attention
- Altered memory
Heroin: A Century-Old Killer
Few drugs are quite as infamous as heroin. In fact, when most people imagine the worst illicit substance they can think of, heroin is usually at the top of their mind. And that doesn’t come as much of a surprise. This drug has been around since 1890 and has regularly killed thousands of Americans every year. And it’s only getting worse too. From 2002 to 2016, the rate of fatal heroin overdoses has jumped by a whopping 500%. The problem is especially rampant in the State of Washington too.
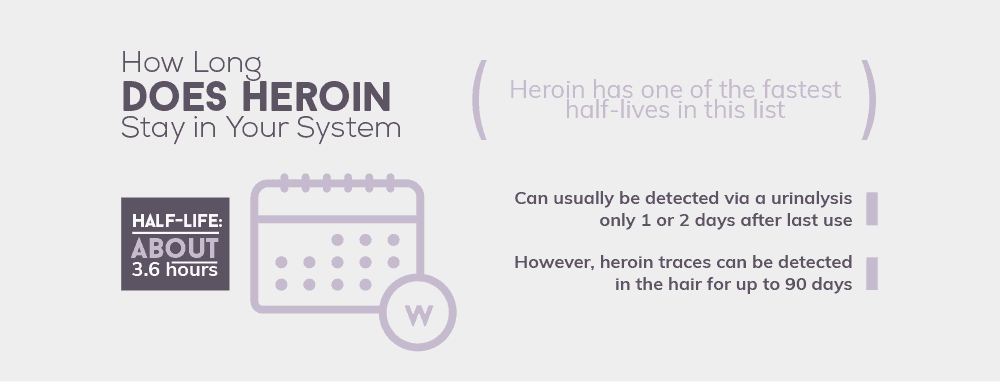
How Long Does Heroin Stay in Your System
Heroin is one of the top illicit drugs that have the fastest half-life. The body clears almost all traces of it within a couple of days, as the half-life ranges from 3 to 30 minutes. The body metabolizes heroin into morphine, and the half-life of morphine is about 3.6 hours. Since the body clears heroin quite quickly, it can be difficult to test for this drug. Blood tests will only be accurate if they are done on the same day. This narcotic remains in the urine for 1 to 2 days afterward. The most accurate test would be a hair drug test. Traces of heroin will linger in the hair for up to 90 days.
Side Effects of Abusing Heroin
According to NIDA, there are loads of short-term and long-term heroin side effects including: Short-Term Side Effects
- Dry mouth
- Warm flushing of the skin
- Heavy feeling in the arms and legs
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe itching
- Clouded mental functioning
- Going “on the nod,” a back-and-forth state of being conscious and semiconscious
Long-Term Side Effects
- Insomnia
- Collapsed veins for people who inject the drug
- Damaged tissue inside the nose for people who sniff or snort it
- Infection of the heart lining and valves
- Abscesses (swollen tissue filled with pus)
- Constipation and stomach cramping
- Liver and kidney disease
- Lung complications, including pneumonia
- Mental disorders such as depression and antisocial personality disorder
- Sexual dysfunction for men
- Irregular menstrual cycles for women
” column_min_width=”[object Object]” column_spacing=”[object Object]” rule_style=”[object Object]” rule_size=”[object Object]” rule_color=”[object Object]” hide_on_mobile=”[object Object]” class=”[object Object]” id=”[object Object]”][object Object]
Hydromorphone: A Potently Powerful Opioid
Most commonly used under the addictive prescription medication Dilaudid, hydromorphone is another deadly substance that belongs to the opioid class of drugs. It’s about 5 times more powerful than morphine, making it more potent even than other highly-abused opioids like oxycodone or codeine.
How Long Does Hydromorphone Stay in Your System
Like many other opioids, hydromorphone tends to stay in the body for a bit longer than other drugs. This opioid, in particular, has a half-life of just 2 to 3 hours. When it comes to the various testing methods that are used to detect it, Very Well Mind reports that hydromorphone abuse can be noticed in the:
- Urine for 3 to 4 days
- Blood for up to 24 hours
- Saliva for up to 2 days
- Hair for up to 90 days
Side Effects of Hydromorphone Abuse
According to MedlinePlus, some short-term and long-term side effects of abusing hydromorphone may include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Headache
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Dry mouth
- Lightheadedness
- Drowsiness
- Heavy sweating
- Muscle, back or joint pain
- Stomach pain
- Anxiety
- Flushing
- Itching
- Depression
Long-Term Side Effects
- Impaired decision making
- Unusual behaviors and erratic moods
- Poor response to stress
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Serious respiratory disorders
- Cognitive malfunction
Percocet: A Combination Narcotic with Deadly Potential
Another powerful opioid pain reliever, Percocet is a combination drug made from both oxycodone (the active ingredient in drugs like OxyContin) and acetaminophen. This combination increases the potency of the drug as well as the addictive potential. They’re sometimes called “percs” or “bananas” on the street and are snorted, injected, or taken orally just like other opioids.
How Long Does Percocet Stay in Your System
Prescribed to treat moderate to severe pain, Percocet contains both oxycodone and acetaminophen. These two ingredients take varying lengths of time to be cleared from the body. Acetaminophen has a half-life of about 1.25 to 3 hours, and is usually cleared from the body within 24 hours. Oxycodone has a much longer half-life at 3.2 hours. This ingredient is further metabolized into noroxycodone and oxymorphone. The half-life of oxycodone is about 3.2 hours. As a result, Percocet has an average half-life of about 3.5 hours. In most cases, this drug will be completely cleared from the body in about 19 hours. The narcotic is detectable in urine for up to 2 days.
Side Effects of Percocet Abuse
According to NIDA, some of the short-term and long-term side effects of abusing prescription opioids like Percocet include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Euphoria
- Slowed breathing
Long-Term Side Effects
- Increased risk of contracting infectious diseases
- Severe liver failure
- Cognitive difficulties
- A slowed metabolism
- A higher risk of becoming addicted to other opioids like heroin
Suboxone: Addiction Medication with a Dark Side
One of the most promising new opioid addiction treatment drugs being used today, Suboxone is a partial opioid agonist that stimulates opioid receptors in the brain, just not to the same degree as other opioids like heroin or oxycodone. However, this drug can also be abused as well, even though it’s mainly used to help addicts recover from their dependency problems. And like methadone, it certainly comes with its own very real risks.
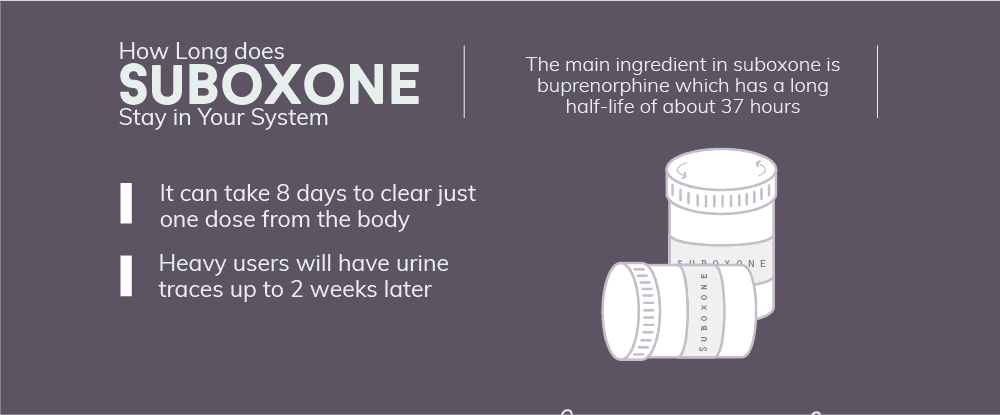
How Long Does Suboxone Stay in Your System
Suboxone is a common drug used to treat opioid addictions. While effective, it can, unfortunately, be misused. Misuse can lead to abuse and addiction. The main active ingredient in this drug is buprenorphine, which has a long half-life of about 37 hours. Due to this reason, it can take the body up to 8 days to clear a single dose of Suboxone. To look for Suboxone, most people use urine tests. The buprenorphine can be detected in urinalysis as soon as 40 minutes after the last dose. It can also remain in the urine for quite some time. Heavy users may still get a positive urine test up to 2 weeks later. Suboxone accumulates in hair follicles as well. A hair test can detect drug use for up to 1 to 3 months.
Side Effects of Suboxone Abuse
Some of the short-term and long-term effects of buprenorphine include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Chills
- Cough
- Feeling faint, dizzy, or lightheaded
- Feeling of warmth or heat
- Fever
- Flushing or redness of the skin, especially on the face and neck
- Headache
- Hoarseness
- Lower back or side pain
- Painful or difficult urination
- Sweating
Long-Term Side Effects
- Drowsiness
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Confusion/disorientation
- Constipation
- Social isolation
- Nausea/vomiting
- Decreased tolerance for pain
Alcohol: America’s Favorite Addictive Substance
Alcohol is without a doubt the most culturally acceptable addictive substance today. People drink it with lunch, dinner, and even breakfast in some circles. However, it’s also one of the deadliest drugs available as well. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Addiction (NIAAA), almost one-fourth of all deaths among 20 to 39-year-olds are related to alcohol. On top of that, new studies suggest that alcohol is definitively the leading cause of death and disease worldwide.
How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Your System
The rate at which the body clears alcohol will depend on the amount of alcohol consumed. It is also dependent on how healthy the drinker’s liver is. Essentially, it takes the liver about an hour to metabolize and clear one ounce of alcohol from the body. One ounce of alcohol results in a blood alcohol level of about 0.015. With this in mind, it’s easy to calculate the length of time it takes for alcohol to leave the body. The legal blood alcohol level for drivers is 0.08. This works out to approximately 5 ounces of liquor. It takes approximately 5.5 hours for this much alcohol to leave the body. Alcohol will also accumulate in the body depending on how quickly one is drinking. At high concentrations, alcohol gets absorbed into the blood and fatty tissues. This usually starts to happen once the blood alcohol level exceeds 0.055. Alcohol absorption rates slow down with the presence of food. It’s not unusual for many Americans to binge drink. After all, binge drinking is defined as for men as 5 or more drinks on one occasion. For women, a binge drinking session is any occasion where 4 or more drinks are involved.
Side Effects of Alcohol Abuse
According to the NIAAA, some of the short-term and long-term side effects of alcohol abuse include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Blackouts
- Poor coordination
- Impaired judgment
- Unconsciousness
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Coma
- Distorted vision
Long-Term Side Effects
- Stretching and drooping of heart muscle
- Brain damage
- Irregular heartbeat
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Fatty liver
- Poor coordination and cognitive ability
- Various kinds of cancers
Valium: A Benzo with a Bite
Valium, more technically known as diazepam, is a powerful benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety, muscle spasms, and even seizures. And while it has a very legitimate and very helpful use in the medical community, it’s also become a drug that’s widely abused for its calming and tranquil effects. Plus, some abusers also mix it with other drugs like alcohol or opioids (which is especially dangerous) in order to intensify their effects.
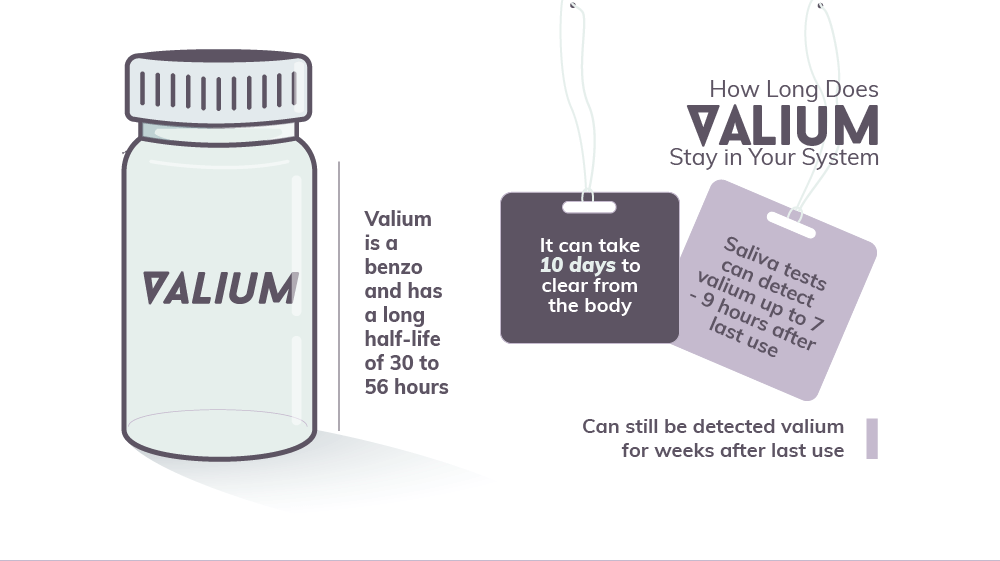
How Long Does Valium Stay in Your System
Valium is one of the most commonly abused prescription medications. It falls under the benzodiazepine class. In comparison to other prescription medications, Valium has a long half-life. It can take anywhere from 30 to 56 hours for 50% of the drug to be removed from the body. Due to this reason, it can approximately 10 days for all traces of Valium to leave the body. This doesn’t include the different metabolites that come from taking the prescription medication. It takes the liver much longer to get rid of these agents. Saliva tests for Valium can detect the drug for up to 7 to 9 days after its last use. Blood tests also offer a similar timeframe; however, it is usually only recommended for long-term users. Urine tests can detect the presence of Valium for weeks after the last use. Valium can also accumulate easily in hair follicles. It can be detected for up to 90 days.
Side Effects of Abusing Valium
According to the DEA (short-term) and Professor Heather Ashton (long-term), some of the most notable side effects of Valium abuse include: Short-Term Side Effects
- Motor incoordination
- Anterograde amnesia
- Slurred speech
- Restlessness
- Delirium
- Aggression
- Depression
- Hallucinations
- Paranoia
Long-Term Side Effects
- Memory impairment
- Paradoxical stimulant effects (anxiety, insomnia, hallucinations, etc.)
- Depression
- Emotional blunting
- Reduced memory
Testing for Drugs
Most of the top 10 illicit drugs will remain in the body for quite some time. Due to this reason, you should always get a drug test done if you suspect a family member or friend of using narcotics. Drug tests are quite inexpensive. Some will even provide instant results. Get more information about drug addictions by contacting one of our counselors. If someone close to you is an addict, this is one of the first places where you’ll want to seek help from. We have a wide array of treatment plans available. With our help, they’ll break free from the shackles of addiction, and have control over their lives again. They’ll be able to detox safely and learn how to deal with their triggers to avoid relapsing. We have all of the resources that they’ll need to get sober.
What Did you Think About This Blog?
Give it a Rating!